Essential Guide to Upgrading Your Electrical Panel: Key Signs and Considerations
Understanding the Basics of Electrical Panels
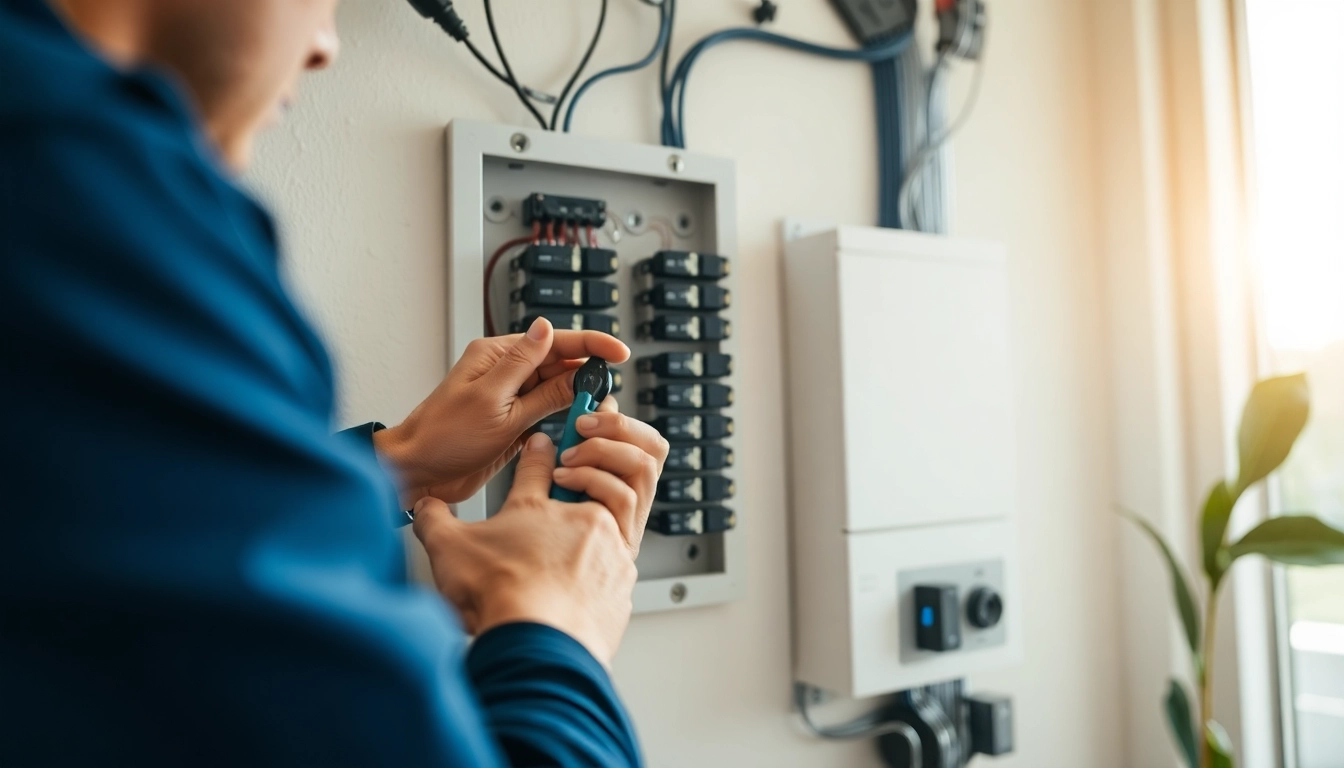
Every home relies on an Electrical Panel as a fundamental part of its electrical system. Sometimes referred to as a breaker box or service panel, this critical component distributes electricity from the main line to individual circuits throughout your home. Understanding how it works, its components, and its importance is essential for homeowners, especially those contemplating an upgrade or installation.
What is an Electrical Panel?
An electrical panel acts as the hub of your home’s electrical system. It receives power from the utility company and distributes electrical energy through various circuits that serve different areas or appliances in your home. Essentially, it regulates and controls the electrical flow to ensure safety and efficiency, preventing overloads that could lead to electrical fires.
Components of an Electrical Panel
Understanding an electrical panel’s components can help demystify its function. Here are the main parts:
- Main Breaker: This is a switch that turns electricity on and off to the entire home. It helps protect the home from overload currents.
- Branch Circuit Breakers: These smaller breakers protect individual circuits within the home. If a circuit becomes overloaded, the breaker will trip, cutting off power.
- Bus Bars: Made of copper or aluminum, bus bars distribute electrical current to the branch circuit breakers.
- Grounding System: This system ensures the electrical panel is grounded properly, which is crucial for safety.
- Service Disconnect: A safety feature to quickly disconnect all electrical supply in emergencies.
How Electrical Panels Function
The operation of an electrical panel is relatively straightforward, yet it plays a vital role in the electrical system. Power from the utility company’s lines enters the panel through the main line and is routed to the main breaker. From there, electricity is distributed to various branch circuit breakers, which each power different parts of the home—such as lights, outlets, and appliances. This process works in conjunction with the grounding system, ensuring that any excess current, particularly during surges or faults, is diverted safely away.
Signs That Indicate It’s Time to Upgrade Your Electrical Panel
With increasing energy demands from modern appliances and technology, many homeowners may find their existing electrical panel inadequate. Recognizing the signs of wear or inefficiency is crucial.
Frequent Circuit Breaker Trips
If you find yourself frequently resetting your circuit breakers, it’s a clear sign that your panel may not be equipped to handle your home’s electrical load. This could be due to overloading, which occurs when too many devices draw power from a single circuit. Over time, frequent tripping can damage the breakers, leading to further complications.
Inadequate Power Supply for Your Needs
Older homes often have electrical panels rated for lower amperages, which can restrict their ability to power modern devices. For instance, if your panel is only rated for 100 amps, but your household demands 200 amps due to various high-energy devices, you may experience performance issues such as dimming lights or slow appliance operation.
Signs of Wear and Tear
Physical signs of wear on the electrical panel, such as rust, scorch marks, or burnt components, indicate it may be time for an upgrade. These defects can lead to dangerous situations, including electrical fires or system failures. Regular inspections by a qualified electrician are essential to catch these issues early.
Types of Electrical Panels Available
When considering an electrical panel upgrade, it’s essential to understand the types available on the market and their respective features.
Standard vs. Smart Electrical Panels
Standard electrical panels have served homes effectively for generations, but smart electrical panels are becoming more common. Smart panels offer advanced features, such as energy consumption monitoring, real-time usage statistics, and the capability to control individual circuits through a mobile app. These innovations can improve energy efficiency and safety, making them attractive for tech-savvy homeowners.
Panel Size and Amperage Options
Electrical panels come in various sizes and amperage ratings, which can be tailored to meet different household needs. Common options include:
- 100 Amp Panels: Suitable for small homes or apartments with minimal electrical demand.
- 150 Amp Panels: A versatile choice for moderate-sized homes that may contain multiple high-power appliances.
- 200 Amp Panels: A standard choice for larger homes or those with high energy demands, providing ample capacity for additional appliances and technology.
Comparing Brands and Models
When upgrading your electrical panel, it’s important to evaluate different brands and models. Popular manufacturers like Square D and Siemens have established reputations for reliability and innovation. Consumers often choose models based on circuit configuration, ease of installation, and warranty options. Reviewing comparative product specifications online can assist in making an informed decision.
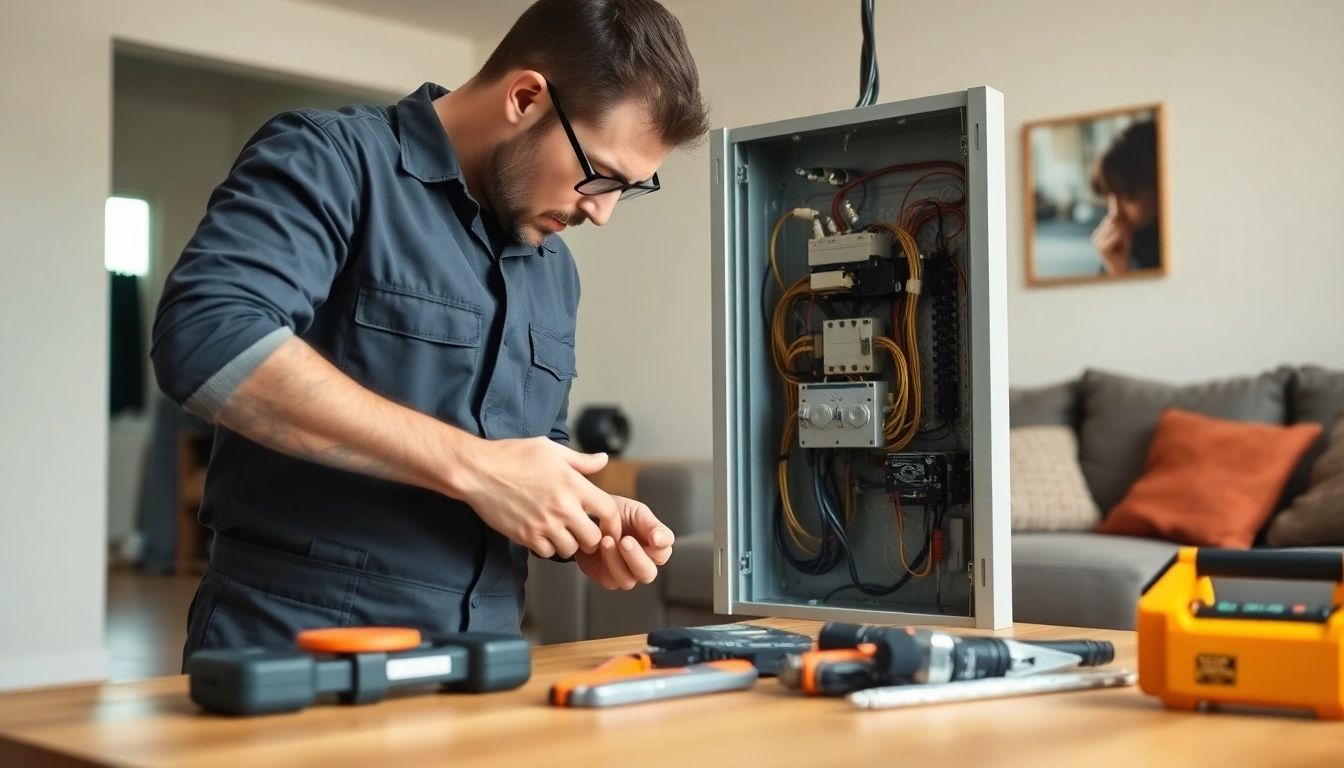
Upgrading Your Electrical Panel: Steps to Follow
Upgrading your electrical panel is not only a necessary action for safety and efficiency but it can also increase your home’s value. Follow these steps to ensure a successful upgrade.
Consulting with a Licensed Electrician
Engaging a licensed electrician is crucial in the upgrade process. An expert will assess your current system, determine your household power needs, and recommend the best panel upgrade options. They will also handle all necessary permits and ensure compliance with local codes, safeguarding the installation process.
Preparing Your Home for the Upgrade
Before the upgrade, your electrician may need to upgrade the home wiring and verify the functionality of any existing circuits. Clearing the area around your electrical panel is essential to allow easy access for the electrician. Additionally, inform your household about potential power interruptions during the installation.
Cost Considerations and Financial Options
The cost to upgrade an electrical panel can vary greatly typically ranging from $800 to $3,000, depending on variables such as the panel size, brand, and labor costs in your area. Discussing your financial options with your electrician may reveal potential savings opportunities, such as energy efficiency rebates or financing plans. It’s essential to budget according to your needs while keeping safety and quality in mind.
Maintaining Your New Electrical Panel
Once your new electrical panel is installed, maintenance becomes paramount to ensure its longevity and reliability. Understanding proper care and recognizing potential issues can help prevent future problems.
Regular Inspections and Maintenance Practices
Scheduled inspections with a licensed electrician should be part of your regular home maintenance. Checkups help identify potential electrical hazards, ensure that breakers are functioning correctly, and confirm that the panel remains free from dust and debris. Homeowners should also keep an eye out for any unusual odors or sounds coming from the panel, as these can signal faults.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Despite a thorough installation, some common issues may still arise. For example:
- Breaker Trips: If breakers are constantly tripping, it may indicate overloaded circuits or faulty appliances.
- Panel Buzzing: A buzzing noise from the panel can indicate loose connections or a malfunctioning breaker.
- Signs of Damage: Look for discoloration or heat emanating from the panel, which can signal serious problems requiring immediate professional attention.
Maximizing Efficiency and Safety
To optimize the performance of your electrical panel, consider energy-efficient practices. This includes using LED lighting, smart home technologies to monitor energy use, and unplugging devices when not in use. Implementing such strategies reduces overall load on your electrical system, promoting safety and efficiency while potentially lowering energy bills.











Post Comment